AIA Ohio Affordable Green Home Design CompetitionSponsor: AIA Trust Type: open, 1-stage Language: English Registration fee:
AIA Associate Member – $25 (early registration)/$50 (late registration)
Non-AIA unregistered – $35 (early registration)/$70 (late registration)
AIA Member – $50 (early registration)/$100 (late registration)
Non-AIA registered architect – $75 (early registration)/$150 (late registration) Eligibility:
All design professionals who have graduated from a school of architecture and have been out of school 10 years or less. Entrants that are not licensed to practice architecture in the State of Ohio are required to partner with an Ohio licensed architect or firm. Awards:
1st Prize in category – $1,000
2nd Prize in category – $500
3rd Prize in category – $250 1st Prize overall – $2,000
2nd Prize overall – $1,000
3rd Prize overall – $500 Timetable:
31 July, 2009 – early registration deadline
14 August, 2009 – late registration deadline
28 August, 2009 – submission deadline
21 September, 2009 – category winners announced
1-3 October, 2009 – overall winners announced Jury:
American Institute of Architects: TBD
Habitat for Humanity: TBD Design Challenge:
A new prototypical house design based upon identified Habitat for Humanity considerations and the AIA Committee On The Environment green design principles. After the competition, the intent is to develop construction documents and build each of the winning designs. Habitat homes are built by volunteers (essentially unskilled labor), and thus the construction documents should be considerably more extensive than typical drawing submissions. The construction drawings must be thorough, fully detailed, and able to receive municipal approval with little to no additional effort required by Habitat for Humanity.
Designs should be region-specific but not site-specific. Priority will be given to flexible designs that are applicable to various site conditions such as lot sizes, topography, orientation, etc.
The home shall be judged on its integration of environmental strategies concerning their impact on the site, water efficiency, energy use, material use, and indoor environmental quality. More specifically in regards to energy use, the minimum energy performance level of the home shall meet the Architecture 2030 Challenge 2010 target of 52 on the HERS index.
entries are expected to address specific issues as it relates to the following:
Affordability – The home shall be affordable to build and maintain.
Context – The design shall reflect the social and economic character of the communities in which the home will be built.
Energy Efficiency – The minimum performance level of the home shall meet the Architecture 2030 Challenges 2010 target of 52 on the HERS index.
Occupant Health – VOC and other know harmful products are to be avoided in the home.
Sustainability – The design shall consider the home’s impact on the immediate and surrounding environment by taking into consideration the use of resource efficient building materials, and resource conserving features. For more information, go to: http://www.aiaohiogreenhome.com/index.html
Email: aiaohio@assnoffices.com |

1st Place: Zaha Hadid Architects – night view from river – Render by Negativ
Arriving to board a ferry boat or cruise ship used to be a rather mundane experience. If you had luggage, you might be able to drop it off upon boarding, assuming that the boarding operation was sophisticated enough. In any case, the arrival experience was nothing to look forward to. I recall boarding the SS United States for a trip to Europe in the late 1950s. Arriving at the pier in New York, the only thought any traveler had was to board that ocean liner as soon as possible, find one’s cabin, and start exploring. If you were in New York City and arriving early, a nearby restaurant or cafe would be your best bet while passing time before boarding. Read more… Young Architects in Competitions When Competitions and a New Generation of Ideas Elevate Architectural Quality 
by Jean-Pierre Chupin and G. Stanley Collyer
published by Potential Architecture Books, Montreal, Canada 2020
271 illustrations in color and black & white
Available in PDF and eBook formats
ISBN 9781988962047
Wwhat do the Vietnam Memorial, the St. Louis Arch, and the Sydney Opera House have in common? These world renowned landmarks were all designed by architects under the age of 40, and in each case they were selected through open competitions. At their best, design competitions can provide a singular opportunity for young and unknown architects to make their mark on the built environment and launch productive, fruitful careers. But what happens when design competitions are engineered to favor the established and experienced practitioners from the very outset? This comprehensive new book written by Jean-Pierre Chupin (Canadian Competitions Catalogue) and Stanley Collyer (COMPETITIONS) highlights for the crucial role competitions have played in fostering the careers of young architects, and makes an argument against the trend of invited competitions and RFQs. The authors take an in-depth look at past competitions won by young architects and planners, and survey the state of competitions through the world on a region by region basis. The end result is a compelling argument for an inclusive approach to conducting international design competitions. Download Young Architects in Competitions for free at the following link: https://crc.umontreal.ca/en/publications-libre-acces/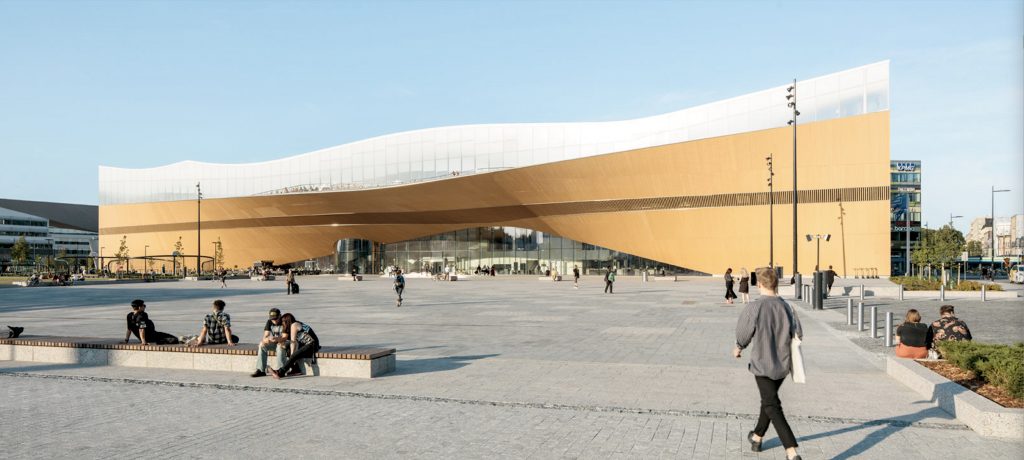 
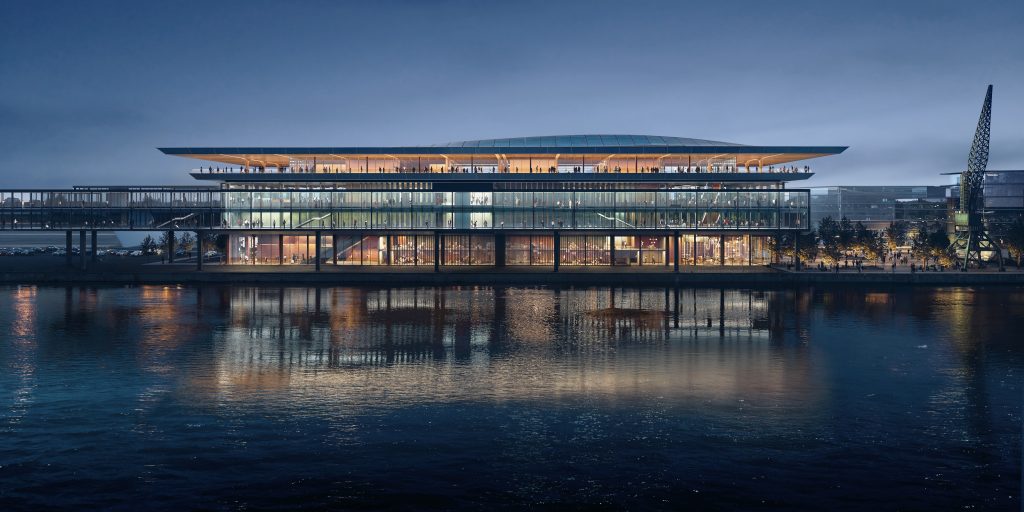
Helsinki Central Library, by ALA Architects (2012-2018)
The world has experienced a limited number of open competitions over the past three decades, but even with diminishing numbers, some stand out among projects in their categories that can’t be ignored for the high quality and degree of creativity they revealed. Included among those are several invited competitions that were extraordinary in their efforts to explore new avenues of institutional and museum design. Some might ask why the Vietnam Memorial is not mentioned here. Only included in our list are competitions that were covered by us, beginning in 1990 with COMPETITIONS magazine to the present day. As for what category a project under construction (Science Island), might belong to or fundraising still in progress (San Jose’s Urban Confluence or the Cold War Memorial competition, Wisconsin), we would classify the former as “built” and wait and see what happens with the latter—keeping our fingers crossed for a positive outcome. Read More… 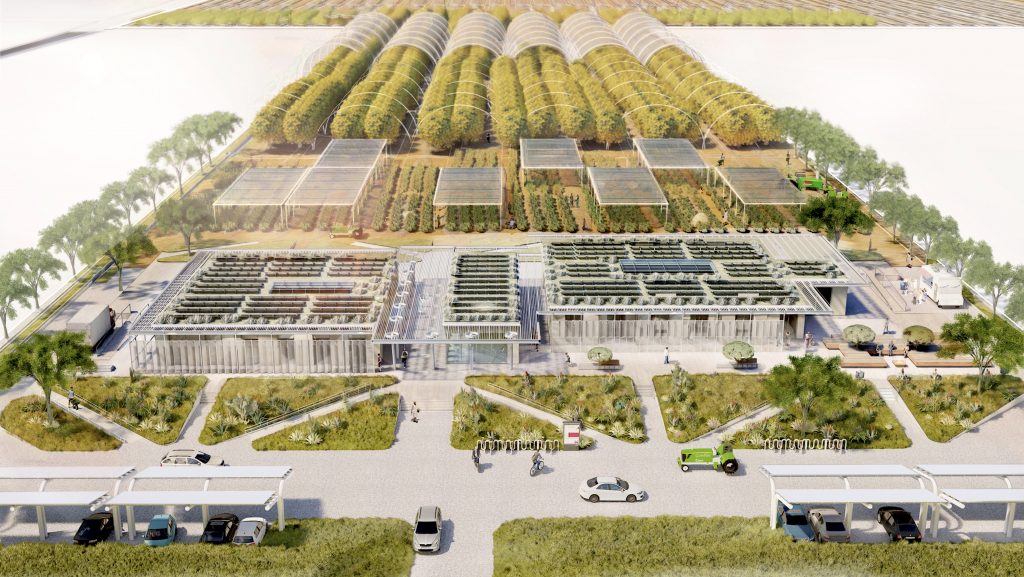
2023 Teaching and Innovation Farm Lab Graduate Student Honor Award by USC (aerial view)
Architecture at Zero competitions, which focus on the theme, Design Competition for Decarbonization, Equity and Resilience in California, have been supported by numerous California utilities such as Southern California Edison, PG&E, SoCAl Gas, etc., who have recognized the need for better climate solutions in that state as well as globally. Until recently, most of these competitions were based on an ideas only format, with few expectations that any of the winning designs would actually be realized. The anticipated realization of the 2022 and 2023 competitions suggests that some clients are taking these ideas seriously enough to go ahead with realization. Read more…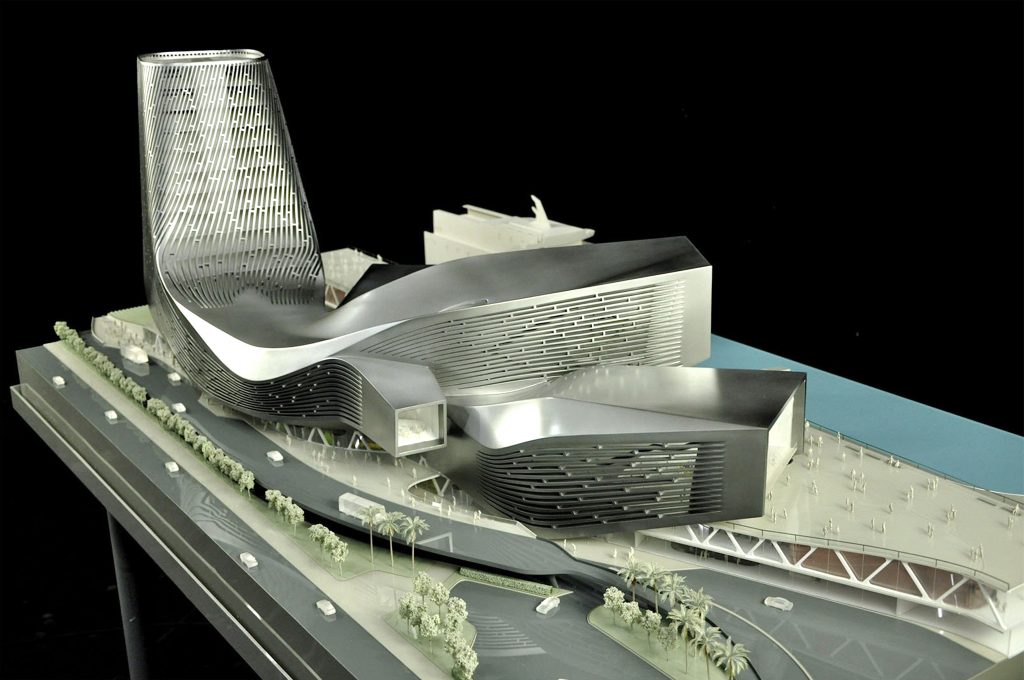 
RUR model perspective – ©RUR
New Kaohsiung Port and Cruise Terminal, Taiwan (2011-2020)
Reiser+Umemoto RUR Architecture PC/ Jesse Reiser – U.S.A.
with
Fei & Cheng Associates/Philip T.C. Fei – R.O.C. (Tendener)
This was probably the last international open competition result that was built in Taiwan. A later competition for the Keelung Harbor Service Building Competition, won by Neil Denari of the U.S., the result of a shortlisting procedure, was not built. The fact that the project by RUR was eventually completed—the result of the RUR/Fei & Cheng’s winning entry there—certainly goes back to the collaborative role of those to firms in winning the 2008 Taipei Pop Music Center competition, a collaboration that should not be underestimated in setting the stage for this competition Read more… 
Winning entry ©Herzog de Meuron
In visiting any museum, one might wonder what important works of art are out of view in storage, possibly not considered high profile enough to see the light of day? In Korea, an answer to this question is in the making. It can come as no surprise that museums are running out of storage space. This is not just the case with long established “western” museums, but elsewhere throughout the world as well. In Seoul, South Korea, such an issue has been addressed by planning for a new kind of storage facility, the Seouipul Open Storage Museum. The new institution will house artworks and artifacts of three major museums in Seoul: the Seoul Museum of Modern Art, the Seoul Museum of History, and the Seoul Museum of Craft Art.
Read more… |