New England Town Meeting HallSponsor: AIA Vermont Emerging Professionals Network. Type: Open, one-stage (see “Eligibility”) Eligibility: This competition is open to all emerging design professionals within 10 years of graduation or 5 years of licensure, living or working in New England. Entrants may either work individually or as part of a team. Fee: $20 Timetable 4 October 2015 – Registration & Submission deadline AWARDS
1st Place: $1000
2nd Place: $500
3rd Place: $250 Background
Only 35.9% of eligible voters in the U.S. cast ballots during the 2014 midterm elections*. That was both the lowest turnout and the biggest drop from a preceding presidential election since 1952*. While many factors contributed to this statistic, the role of architecture can not be diminished.
Many towns hold voting and meetings in inadequate spaces, such as cramped town halls, gymnasiums, and church basements. Communities need a new platform to facilitate and celebrate civic engagement. New England already has a strong tradition of holding annual Town Meetings, where citizens publicly discuss and vote on issues. Proposals should consider the Town Meeting as a framework for architecture that encourages an open dialogue among citizens.
BUILDING REQUIREMENTS
Town Meeting Halls may be sited in any New England community in a prominent location. The two primary functions of Hall are: town assembly and informing the public about local and national issues. Halls should be designed to accommodate: local debates, televised state and national debates, hold community meetings, etc.
The Hall shall consist of a large assembly space, adequate bathrooms, and mechanical space. The Hall shall be appropriately sized to the community it serves. As a rule of thumb 10% of the local voting population might be accommodated in the assembly space at one time. Bathrooms should be sized in relation to assembly capacity. Buildings must meet local codes and comply with ADA requirements.
Design Criteria
• How is the building sited to maximize visibility in town and promote accessibility?
• How might the form and facade of the Meeting Hall communicate function and democratic ideals?
• What are the limitations of traditional meeting spaces that are being improved upon?
• How can architecture encourage voter turnout and engagement in local issues?
The jury will be asked to consider graphic clarity, originality in response to the brief, and cohesiveness of concept. Include a description of approximately 200 words, of the concept, on the board itself. Be concise and clear to convey the essence of the proposal. SUBMISSION REQUIREMENTS
All submissions must be digital. Email a single, horizontally oriented, 18 in x 36 in file, in JPG or PDF format. Please title the file yourname.JPG or .PDF. Indicate entrant name(s), firm affiliation, town/city, and state in the email. Do not include entrant name(s) anywhere on the board itself. Names will be displayed during exhibitions, but will be anonymous during the jury process.
For more information:
Email: AIAVT.EP@Gmail.com
Website: www.AIAVT.org/Emerg-Prof
Facebook: Search for AIAVT-EPN
|
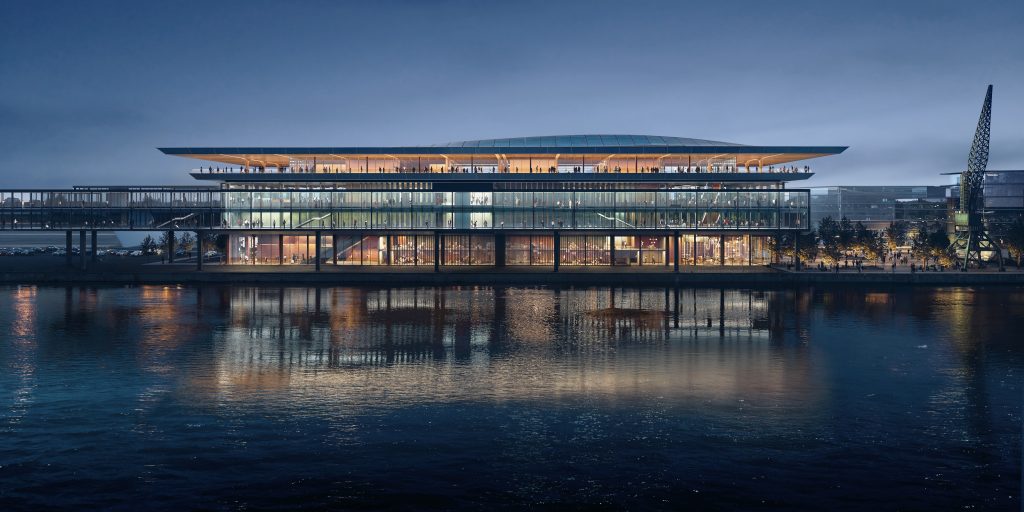

1st Place: Zaha Hadid Architects – night view from river – Render by Negativ
Arriving to board a ferry boat or cruise ship used to be a rather mundane experience. If you had luggage, you might be able to drop it off upon boarding, assuming that the boarding operation was sophisticated enough. In any case, the arrival experience was nothing to look forward to. I recall boarding the SS United States for a trip to Europe in the late 1950s. Arriving at the pier in New York, the only thought any traveler had was to board that ocean liner as soon as possible, find one’s cabin, and start exploring. If you were in New York City and arriving early, a nearby restaurant or cafe would be your best bet while passing time before boarding. Read more… Young Architects in Competitions When Competitions and a New Generation of Ideas Elevate Architectural Quality 
by Jean-Pierre Chupin and G. Stanley Collyer
published by Potential Architecture Books, Montreal, Canada 2020
271 illustrations in color and black & white
Available in PDF and eBook formats
ISBN 9781988962047
Wwhat do the Vietnam Memorial, the St. Louis Arch, and the Sydney Opera House have in common? These world renowned landmarks were all designed by architects under the age of 40, and in each case they were selected through open competitions. At their best, design competitions can provide a singular opportunity for young and unknown architects to make their mark on the built environment and launch productive, fruitful careers. But what happens when design competitions are engineered to favor the established and experienced practitioners from the very outset? This comprehensive new book written by Jean-Pierre Chupin (Canadian Competitions Catalogue) and Stanley Collyer (COMPETITIONS) highlights for the crucial role competitions have played in fostering the careers of young architects, and makes an argument against the trend of invited competitions and RFQs. The authors take an in-depth look at past competitions won by young architects and planners, and survey the state of competitions through the world on a region by region basis. The end result is a compelling argument for an inclusive approach to conducting international design competitions. Download Young Architects in Competitions for free at the following link: https://crc.umontreal.ca/en/publications-libre-acces/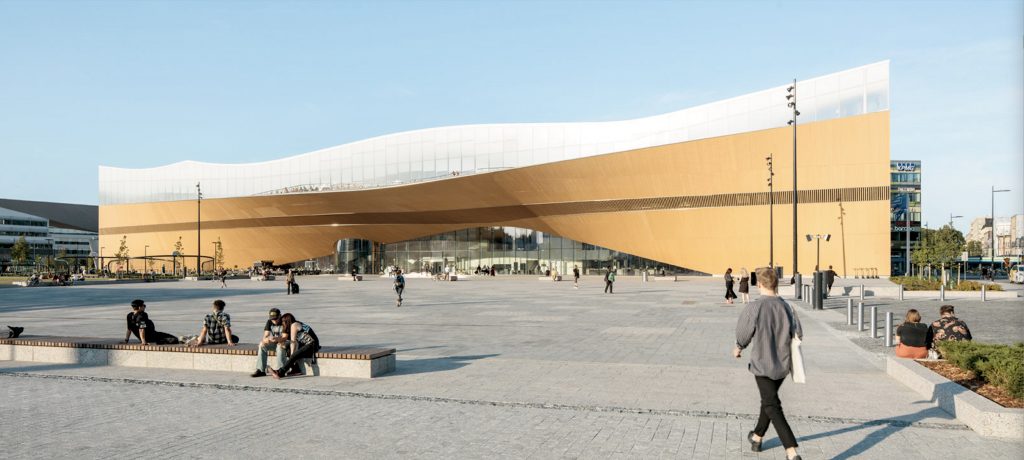 
Helsinki Central Library, by ALA Architects (2012-2018)
The world has experienced a limited number of open competitions over the past three decades, but even with diminishing numbers, some stand out among projects in their categories that can’t be ignored for the high quality and degree of creativity they revealed. Included among those are several invited competitions that were extraordinary in their efforts to explore new avenues of institutional and museum design. Some might ask why the Vietnam Memorial is not mentioned here. Only included in our list are competitions that were covered by us, beginning in 1990 with COMPETITIONS magazine to the present day. As for what category a project under construction (Science Island), might belong to or fundraising still in progress (San Jose’s Urban Confluence or the Cold War Memorial competition, Wisconsin), we would classify the former as “built” and wait and see what happens with the latter—keeping our fingers crossed for a positive outcome. Read More… 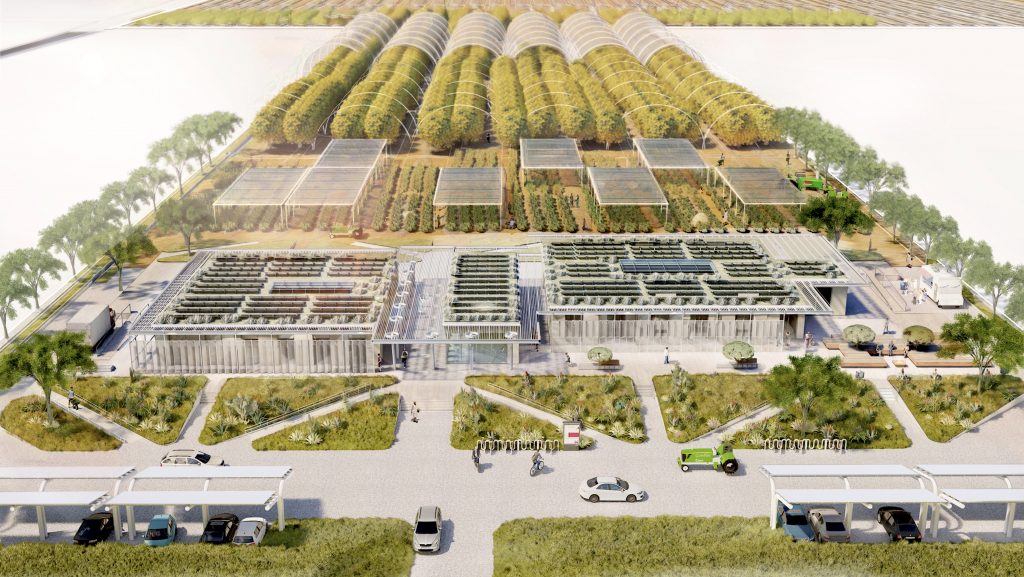
2023 Teaching and Innovation Farm Lab Graduate Student Honor Award by USC (aerial view)
Architecture at Zero competitions, which focus on the theme, Design Competition for Decarbonization, Equity and Resilience in California, have been supported by numerous California utilities such as Southern California Edison, PG&E, SoCAl Gas, etc., who have recognized the need for better climate solutions in that state as well as globally. Until recently, most of these competitions were based on an ideas only format, with few expectations that any of the winning designs would actually be realized. The anticipated realization of the 2022 and 2023 competitions suggests that some clients are taking these ideas seriously enough to go ahead with realization. Read more…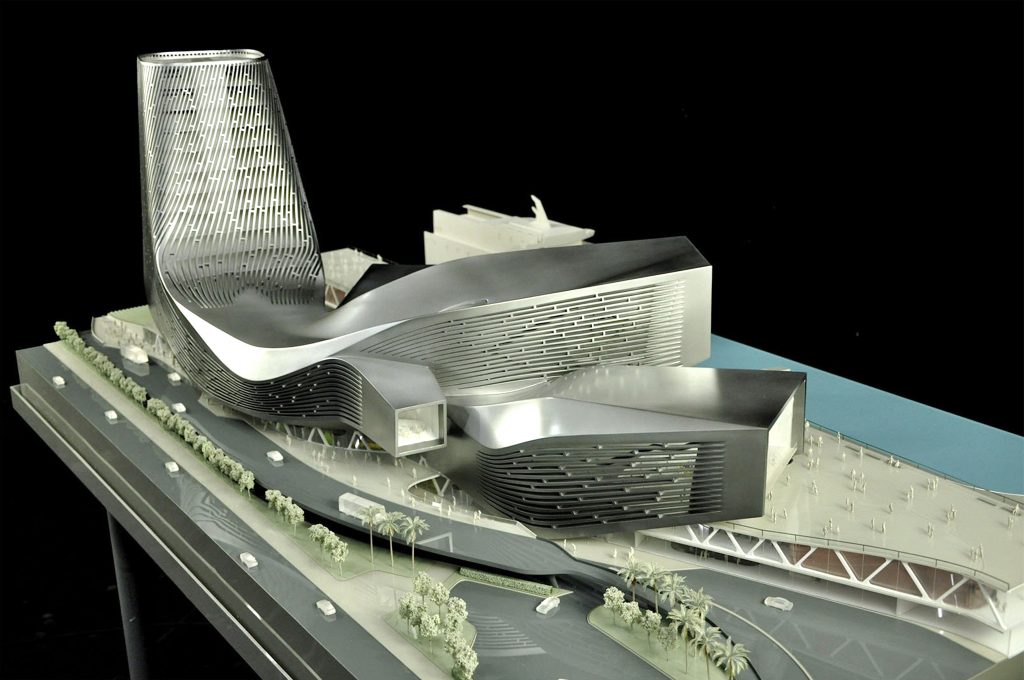 
RUR model perspective – ©RUR
New Kaohsiung Port and Cruise Terminal, Taiwan (2011-2020)
Reiser+Umemoto RUR Architecture PC/ Jesse Reiser – U.S.A.
with
Fei & Cheng Associates/Philip T.C. Fei – R.O.C. (Tendener)
This was probably the last international open competition result that was built in Taiwan. A later competition for the Keelung Harbor Service Building Competition, won by Neil Denari of the U.S., the result of a shortlisting procedure, was not built. The fact that the project by RUR was eventually completed—the result of the RUR/Fei & Cheng’s winning entry there—certainly goes back to the collaborative role of those to firms in winning the 2008 Taipei Pop Music Center competition, a collaboration that should not be underestimated in setting the stage for this competition Read more… 
Winning entry ©Herzog de Meuron
In visiting any museum, one might wonder what important works of art are out of view in storage, possibly not considered high profile enough to see the light of day? In Korea, an answer to this question is in the making. It can come as no surprise that museums are running out of storage space. This is not just the case with long established “western” museums, but elsewhere throughout the world as well. In Seoul, South Korea, such an issue has been addressed by planning for a new kind of storage facility, the Seouipul Open Storage Museum. The new institution will house artworks and artifacts of three major museums in Seoul: the Seoul Museum of Modern Art, the Seoul Museum of History, and the Seoul Museum of Craft Art.
Read more… |